
by vCare Project Management CW | Jul 24, 2025 | Leadership in Project Management, Portfolio Management, Program Management, Project Management
Introduction
Project Management Offices (PMOs) are more than just administrative hubs in today’s busy business world. Businesses can adapt, provide value, and make wise decisions with the support of these strategic drives. As businesses look for professionals capable of spearheading this transformation, the PMI-PMOCP™ (PMO Certified Professional) has emerged as a highly regarded certification confirming both strategic insight and PMO leadership.
With the help of useful frameworks and leadership skills, PMI-PMI-PMOCP™ enables professionals to create, run, and develop PMOs that support organizational objectives. It positions certified leaders as important forces behind corporate transformation by signifying a change from traditional project oversight to strategic value delivery.
This article offers a detailed guide on obtaining the PMI-PMOCP™ certification, covering the exam layout, study schedule creation, leadership development, PMO capacity improvement, and finding resources and prep tools. It emphasizes the importance of developing leadership skills, improving PMO capacity with actual knowledge, and finding practical exam-day advice to maximize the certification’s impact on your career.
Unlocking career potential with PMI-PMOCP™
The growing focus on value-driven delivery and strategic alignment across businesses is changing the function of PMOs. Through specialised credentials like the PMI-PMOCP™, this shift has created a fantastic opportunity for people to progress in their careers. The certification attests to a deep understanding of PMO operations, governance frameworks, and business integration and is intended for PMO executives, team members, and portfolio professionals.
The PMI-PMOCP™ is a strategic facilitator for career progression that goes beyond a certification. It prepares professionals for positions influencing corporate decision-making rather than just operating coordination. With this certification, applicants can pursue senior roles that prioritize leadership and stakeholder engagement, such as Head of Strategic Initiatives, Enterprise PMO Manager, or PMO Director. Possessing the PMI-PMOCP™ boosts your reputation and demonstrates to potential employers that you are capable of starting, expanding, and optimizing PMOs for long-term impact in a global job market that is increasingly focused on measurable skills.
According to the Earning Power: Project Management Salary Survey—Twelfth Edition, only 61% of PMOs believe they are successful, and 93% of unbacked PMOs say their value is not understood by executives. These findings highlight the growing need for certified professionals who can lead strategic, value-driven PMOs.
Additionally, the certification promotes professional mobility across sectors and locations for those who want to lead change in complex settings. For seasoned professionals prepared to take on more senior leadership responsibilities, the PMI-PMOCP™ is a wise, forward-thinking investment in career development.
The Role of PMI-PMOCP™ in today’s evolving PMO landscape
The PMI‑PMOCP™ certification is essential for confirming the strategic abilities needed by modern businesses, as PMOs expand beyond their traditional administrative duties.
In a Broadcom survey, 96% of 501 multinational companies said they were becoming more reliant on PMOs to centralise project management and improve value delivery; 98% said they thought PMOs were critical, and 93% said they intended to grow their PMO operations. This modification emphasises the necessity of having skilled professionals lead these next-generation PMOs.
NTT DATA’s “Evolution of the PMO” report highlights how digitally empowered, agile PMOs are evolving into strategic value centres, leveraging analytics and artificial intelligence to improve productivity and decision-making. Because the PMI‑PMOCP™ evaluates all of these skills, these PMOs require leaders with expertise in governance maturity, digital tool execution, and integration with business strategy.
A great example of how they may increase their delivery flexibility is the PMO of Melbourne Airport, which used hybrid systems and became the only provider during COVID-19. By equipping them with the frameworks, stakeholder engagement techniques, and governance understanding required for PMOs in the digital era, certification equips PMO executives to spearhead such transformations.
PMI-PMOCP™ holders are prepared to guide companies through challenging transformation by collaborating closely with strategic portfolio and performance management methodologies. This ensures that PMO activities are not only monitored but also optimized for a company-wide impact.
Advancing from execution to strategy: A career shift enabled by PMI-PMOCP™
Building on this solid base, the PMI-PMOCP™ certification turns into a strong enabler for those trying to move from execution-centered jobs to strategic leadership posts. By arming PMO practitioners with the systems and competencies required to make significant decisions, it bridges the gap between operational delivery and corporate value realization. Experts who are certified manage portfolio priorities, align projects with corporate strategy, and assess results important to executive stakeholders. They are trained to handle tasks beyond the constraints of deadlines and scope. This change makes them as essential to corporate transformation by turning their function from task fulfillment to strategic advice.
In actuality, this change is quite apparent. After receiving PMI-PMOCP™, many professionals formerly in charge of project coordination have moved into roles such as Strategic Realization Office Lead, Director of Enterprise PMO, or Head of Delivery Governance. These positions call for more than just process knowledge; rather, the capacity to influence, negotiate, and generate results consistent with company objectives is required.
PMI-PMOCP™,’s focus on strategy alignment, advantage realization, and maturity models makes this career leap possible. For those seeking substantial expansion, it provides a clear path to influence portfolio-level decisions and lead the business from the front, making the shift from project manager to strategic leader a reality.
A closer look at the exam structure and core domains
The PMI-PMI-PMOCP™ exam is developed to evaluate both theoretical knowledge and practical capabilities since PMO leadership necessitates the development of real-world competencies. It assesses a candidate’s capacity to consciously plan, create, carry out, and improve PMO operations in a range of organizational contexts. Focused research necessitates domain and structural knowledge for subject matter experts.
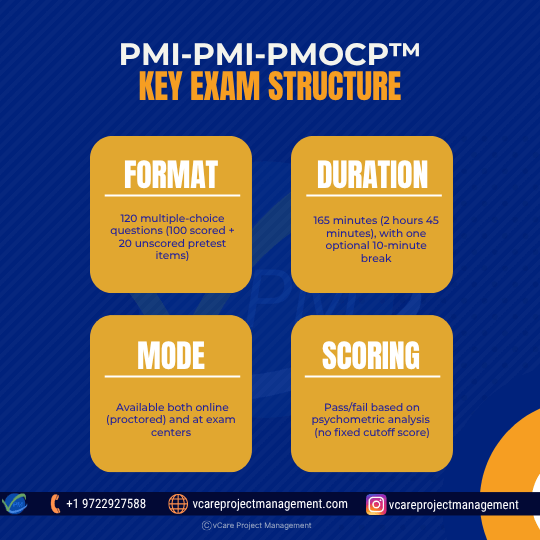
Here’s what you need to know before attempting the PMI-PMOCP exam: 120 questions, 165 minutes, flexible modes, and psychometric scoring.
Core Exam Domains and weightage:
- Organizational Development and Alignment (16%): Focuses on building organizational project management maturity and capability.
- PMO Strategic Elements (18%): Covers PMO vision, mandate, governance, and stakeholder engagement.
- PMO Design and Structuring (18%): Examines service design, customer-centricity, and value proposition.
- PMO Operation and Performance (15%): Assesses service delivery, resource management, and onboarding processes.
- PMO Enhancement and Effectiveness (18%): Emphasizes performance measurement, maturity models, and continuous improvement.
- People (15%): Evaluates leadership, interpersonal skills, and strategic thinking.
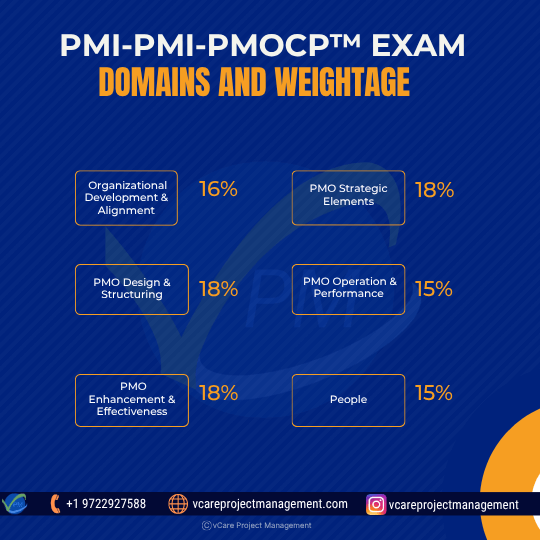
Master the 6 core domains of the PMI-PMOCP exam—get familiar with what matters most and where to focus your preparation.
Successful completion of the exam and practical implementation of ideas in real-world PMO scenarios are prerequisites for a thorough comprehension of these fields.
Designing a Smart Study Plan using the Exam Content Outline (ECO)
Having a well-organised and targeted study plan is essential for passing the PMI-PMOCPTM test. You may be sure that your preparation aligns with the fundamental abilities required of high-performing PMO staff by using the Exam Content Outline (ECO). Because it provides detailed instructions on domains, tasks, and enablers, the ECO is the most reliable place to start when creating your exam strategy.
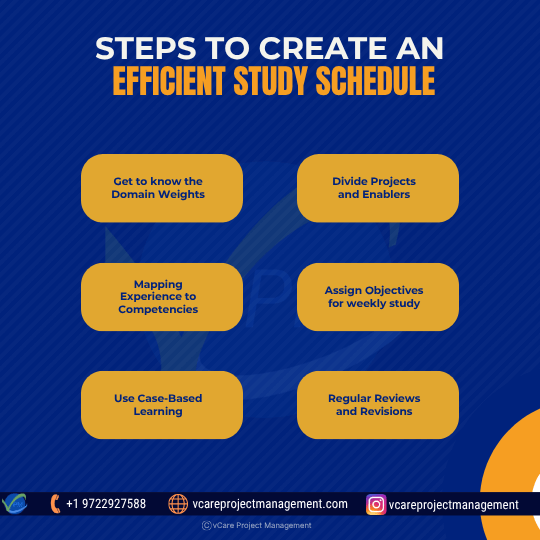
Maximize your PMI-PMOCP prep with this 6-step study plan—prioritize domain weights, apply case-based learning, and grow strategic PMO skills.
Steps to create an efficient study schedule:
- Get to know the Domain Weights: Based on the domain percentage (e.g., PMO Strategic Elements and PMO Design each carry 18%), give study time top focus.
- Divide Projects and Enablers: Translate every domain into actual situations to internalize ideas and gauge practical understanding.
- Mapping Experience to Competencies: Find locations where your hands-on PMO knowledge complements or falls short of ECO job coverage.
- Assign objectives for weekly study: Assign particular domains per week using a calendar, therefore balancing theory review, case analysis, and practical experience.
- Use Case-Based Learning: Deepen your awareness of stakeholder engagement, service design, and performance measures by using case studies and sample scenarios.
- Regular Reviews and Revisions: Set weekly reviews and strengthen underperforming areas found through self-evaluations or mock examinations.
Keeping up with the ECO helps you concentrate on your studies and learning PMO leadership skills that are both career-oriented and relevant to exams.
Growing your strategic thinking and leadership skills
The ECO’s study plan equips candidates with leadership and other critical abilities that go beyond test preparation. The PMI-PMOCP™ certification aids in the development of strategic thinking and leadership skills that are necessary for directing organisational effect through the PMO.

Discover how PMI-PMOCP boosts strategic alignment, risk leadership, stakeholder engagement, and executive presence for PMO professionals.
The PMOCP™ process plays a vital role in supporting leadership and strategic development, like:
- Improves strategic alignment: Enhances your capacity to align portfolio and program results with organizational objectives and long-term vision.
- Develops stakeholder engagement capabilities:Builds stakeholder engagement skills by enhancing communication, negotiating, and relationship-building across executive, functional, and delivery teams.
- Fosters systems thinking: Encourages systems thinking by showing you how to evaluate linkages across projects and portfolios to provide a more expansive viewpoint.
- Enhancing governance and risk leadership: Arms you with instruments to proactively handle strategic risks and set up efficient decision-making systems.
- Supports data-informed decision-making: Encourages the use of key performance indicators and maturity models to drive ongoing improvement.
- Builds executive-level presence:Helps you portray PMO value in business terms and direct influence at the leadership table, establishing an executive-level presence.
Professionals grow into forward-thinking leaders who help the PMO serve as a catalyst for strategy execution and corporate transformation via the PMOCP™ certification process.
Strengthening your PMO capabilities with practical knowledge
Building realistic, hands-on skills is vital as PMOs become strategic allies inside companies. Meant to improve not only theoretical understanding but also the practical application of PMO ideas across a range of business scenarios, the PMI-PMOCP™ certification is also meant to help. By means of its six key domains, the certification assists professionals in enhancing their capacity to plan and run PMOs that match the objectives of the company. Candidates acquire knowledge on how to establish performance measures that show quantifiable impact, execute governance systems, and define distinct PMO service offerings.
Moreover, stressed in the program stresses capacity building via maturity assessments, feedback systems, and continuous improvement approaches. PMO leaders may routinely evaluate success and change their services to meet changing corporate demands using these tools. Furthermore, the certification strengthens core talents in benefit realization, stakeholder management, and resource planning. Professionals become better prepared to head high-performing PMOs supporting both agile and traditional delivery environments by means of this understanding.
The pragmatic frameworks discussed in the PMI-PMOCP™ program help you to develop fit-for-purpose ideas, whether you are building a new PMO or improving one already in place. Maintaining long-term value and positioning the PMO as a reliable strategic player in the company depends on this capacity.
Tools, resources, and prep courses to accelerate your growth
It takes more than just reading to get ready for the PMI-PMOCP™ certification. A strategic plan needs to be backed up by relevant materials, instructional materials, and systematic learning in order to be successful. For PMO experts looking to increase their knowledge and improve their test preparation, using targeted information is essential.
Your preparation route is supported by a number of high-quality materials. These materials make it possible to use concepts in real-world PMO scenarios in addition to passing the exam.
Suggested learning resources and tools include:

Ace the PMI-PMOCP exam with the right resources: ECO, case studies, question banks, and memory aids like flashcards and mind maps.
- Exam Content Outline (ECO): The ECO serves as the foundation for all study plans. It divides areas, chores, and facilitators that you have to learn.
- Case Studies and Real-World Scenarios: Connect theory to real-world PMO decision-making by using industry case studies.
- Practice Exams and Question Banks: Regular exams help expose areas of deficiency and prepare you more effectively for exams using practice exams and question banks.
- Flashcards and Mind Maps: Excellent for remembering concepts, models, and vocabulary via flashcards and Mind Maps.
PMO Capability Maturity Models and Templates: Help you to grasp strategic alignment and operational excellence.
A selection of the best preparation programs:
• Instructor-led boot camps focused on domain-wise learning
• On-demand video lectures enabling flexible study
• Peer discussion groups and study cohorts for collaborative learning
Exploring thought leadership blogs, PMO podcasts, and LinkedIn learning spaces helps bring in wider perspectives and expert insights. The newly launched PMOCP4U LinkedIn group offers a dedicated space for PMO professionals and PMI-PMOCP™ aspirants to connect, exchange resources, and grow together. Building lasting capability in PMO leadership and true exam confidence, depends on combining structured preparation with practical, real-world dialogue
Exam-day confidence: Tips to manage time and approach questions
More than technical ability is needed for success on the day of the exams. It calls for confidence, concentration, and a well-practiced approach. The PMI-PMOCP™ exam seeks to assess your capacity to apply PMO ideas in realistic and sometimes difficult situations as well as your knowledge of PMO concepts.
Time management and a bold approach to the exam are crucial:
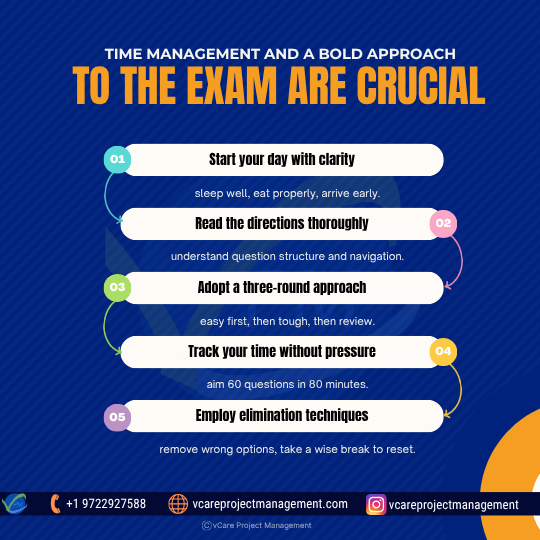
Maximize your exam success with these 5 time-tested PMI-PMOCP strategies—clarity, direction, pacing, and smart elimination.
- Start your day with clarity: If you are taking the exam online, arrive early for check-in or system testing, get a full night’s sleep, and eat properly.
- Read the directions thoroughly: During the first several minutes, get acquainted with the navigation and structure of the questions.
- Adopt a three-round approach: First, respond to questions you are certain of. Second, try rather challenging ones. Last, go back to any questions marked or time-consuming.
- Track your time without pressure:Target to finish the first 60 questions in around 80 minutes, allowing adequate time for the other parts, so monitor your time without pressure.
- Employ elimination techniques: Especially in scenario-based problems, eliminate wrong possibilities to enhance accuracy. Wise optional break: Use this time to refocus and reset for the second half of the exam.
Supported by thorough preparation, a calm and organized approach will enable you to negotiate the exam with confidence and clarity.
From certification to career growth: Making the most of PMI-PMOCP™
Getting the PMI‑PMOCP™ certification is just the first step; true professional development results from your use of it. According to the Master of Project Academy’s recent data, 35. 8% of project-related certified professionals saw a 10% plus salary increase after getting their credentials, and 41. 1% found promotions or new positions. This implies that rather than only validating abilities, certification results in noticeable progress.

PMI-PMOCP isn’t just a certification—it’s your launchpad to leadership, strategic impact, and better pay.
In your role as a PMO specialist, you aim to utilize your qualifications for actual career advancement:
- Highlight measurable results:Show projects where your PMO techniques enhanced performance, governance, or stakeholder satisfaction to position yourself as a business-value driver. Highlight measurable outcomes.
- Aim for strategic PMO roles: Many PMOCP™ holders assume leadership positions like PMO Director, Portfolio Governance Manager, or Head of Delivery Strategy, roles that call for the precise skills indicated by the certification.
- Leverage in job negotiations: Negotiate compensation, role level, or responsibility using achievements linked to credentials. Usually, certified professionals have greater initial pay.
Organizations are also aggressively seeking PMO-certified specialists to bridge the gap between strategy and implementation. Certification like PMOCP™ have genuine market relevance as PMOs more and more promote hybrid delivery, data-driven decision-making, and digital transformation. You must possess not only process-oriented skills but also strategic thinking, data literacy, and an agile mindset.
Action plan for post-certification success:
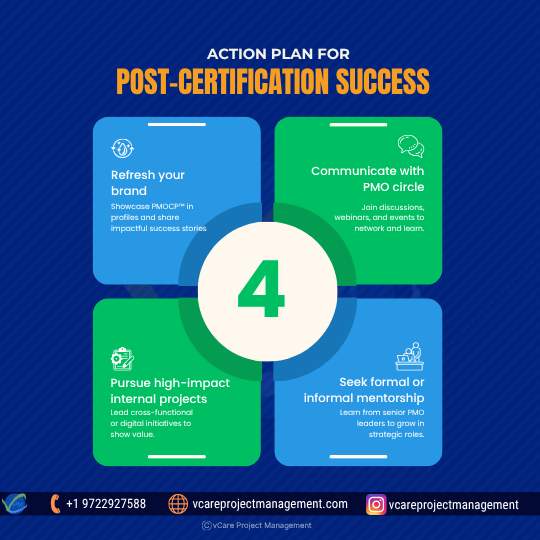
PMOCP™ is just the beginning. These 4 post-certification strategies can define your leadership path and strategic influence.
- Refresh your brand: Build your brand identity by using PMOCP™ on LinkedIn, your resume, and profiles while sharing success stories related to corporate influence.
- Communicate with PMO circle: Take part in PMO-oriented conversations, podcasts & webinars, and more in person to network and share ideas and raise awareness.
- Pursue high-impact internal projects:To show strategic leadership, volunteer for internal cross-functional or digital project programs inside your company.
- Seek formal or informal mentorship:Ask senior PMO leaders for advice on managing strategic roles or growing PMO capacity and look for formal or informal mentorship.
You are not just confirming your abilities by deftly matching your certified skills to organizational needs and highlighting your impact, but also hastening a deliberate move into senior PMO leadership. The PMI PMOCP™ can be the catalyst that changes your career path, thereby converting a certification into permanent professional development.
Conclusion
The PMI-PMOCP™ certification is more than simply a scholastic achievement in today’s evolving PMO landscape; it is a strategic gateway to leadership and professional advancement. From the beginning of the planning process, professionals gain insight on how to maximize stakeholder impact, align PMO duties with company vision, and provide demonstrable value. Through a well-organized study plan, a deep understanding of the Exam Content Outline (ECO), and an emphasis on real-world application, candidates get a mix of knowledge and leadership abilities that are immediately applicable in the workplace.
When experts look into the certification, they find several important questions, such as:
- How does PMI-PMOCP™ distinguish itself from other project management certifications?
- Will this certification enable me to advance to a strategic or leadership position?
- How may I show my employer the advantages of certification?
- Do long-term professional benefits outweigh the time and money invested?
- How can I apply and maintain my knowledge if I pass the examination?
These questions are not only genuine, but they also provide insights from professionals who are about to make important advancements. The answer depends on how the certification is used.
I had the opportunity to speak with PMI’s Kim Marcelliano about the strategic relevance of the PMI-PMOCP™ certification.
Upcoming PMI-PMOCP™ programs led by me will offer a structured path for professionals looking to deepen their PMO capabilities and earn this strategic credential. I’m excited to support and share these initiatives as they unfold.
Upcoming PMI-PMOCP Exam Prep Training 2025:
Online PMI-PMOCP Bootcamp:
- 27–28 September, 9am-5pm, CDT | Link: https://bit.ly/4mrfBHo
- 7-8 November, 7 am – 3 pm CST | Link: https://bit.ly/3FRlr4i
- 15 – 16 November, 9am-5pm, CST | Link: https://bit.ly/4jbZGcY
Direct PMI-PMOCP Bootcamp, Dallas, USA :
- 17-18 November, 9am-5pm, CST | Link: https://bit.ly/3Zqlgn2
- 13-14 December, 9am-5pm CST | Link: https://bit.ly/4drorAA
When used strategically, PMI-PMOCP™ not only validates your expertise but also positions you to drive change, provide value, and shape your company’s future through a productive PMO.
#PMIPMOCP #PMOCertification #PMOLeadership #ProjectManagement #StrategicLeadership #PMOCareer #DharamSingh #vCareProjectManagement #PMIATP #PMOCPExamPrep #PortfolioGovernance #PMOTransformation #ExamSuccess #PMOStudyTools #PMOCPJourney

by vCare Project Management CW | Jul 11, 2025 | Program Management, vCare PMI Certification Training Classes
🎯 Ready to Elevate Your Program Management Career?
Join our exclusive PgMP Bootcamp in Sydney from 15th to 17th August 2025, led by Dharam Singh PfMP, PgMP, PMP, PMOCP, PBA, SP, RMP, ACP, DASM, DASSM, PMI-ATP, the world’s most trusted PgMP® mentor.
With over 576 certified PgMPs, including 57 from Australia, vCare Project Management brings you a proven pathway to PgMP® success.
🔗 Register Now → https://bit.ly/3ZnQ9sy
🕘 Live 9 AM – 5 PM (AEST) | 📍 Sydney | 👥 Direct Classroom Training
Date: 15-17, August 2025
✅ Personalized coaching throughout your journey
🎓 15 expert-led videos + 48 PDUs/Contact Hours
🛠️ End-to-end support: application, audit & panel review
📘 Includes Reference Guide, ECO Mapping Workbook & Mock Test
💡 This is more than a bootcamp – it’s a career transformation experience.

Get certified with confidence! Join the PgMP Bootcamp in Sydney this August 2025—expert training, mock exams, 48 PDUs, and full support included.
Upcoming Direct Classroom Training Programs in Australia:
-> PfMP, 12-14 August 2025, Sydney: https://bit.ly/4n8LdSA
-> PgMP, 18-20 August 2025, Melbourne: https://bit.ly/44DRrkK
-> PfMP, 23-25 August 2025, Melbourne: https://bit.ly/3GfkmUj
“For more details or corporate group bookings, feel free to message us directly or drop a comment below – we’re happy to assist.”
Call us: +1 972 292 7588 / +1 650 283 0123 (U.S.)
Email Id: team@vcareprojectmanagement.com
Free Consultation:
Book a free 15-minute session with Dharam Singh, http://talktodharam.com
#PgMPAustralia #SydneyEvents #ProgramManagement #PMICertification #DharamSingh #vCareSuccess #PgMPExamPrep #PgMPMentor #PMOLeadership #PgMPCertification #StrategicProgramManagement #ProjectLeadership #vCareProjectManagement #PMIATP #ClassroomBootcamp #PgMP2025 #PgMPSydney

by vCare Project Management CW | Jun 28, 2025 | Program Management
🔸 Ready to Crack the PgMP Certification with Confidence? Let’s Make It Happen.
PgMP mock exam 2025 | PgMP practice test online | Program management certification simulator | PMI certification preparation | Best PgMP exam simulator
Take your preparation to the next level with PgMP Challenger Gold from vCare Project Management – a PMI® Authorized Training Partner trusted by professionals in 60+ countries.
🔗 Prepare like it’s the real PgMP® exam. Start now:
https://bit.ly/3NGrysU
🎯 What’s Included:
✔️ 5 Full-Length PgMP® Mock Exams
✔️ 850 High-Quality Practice Questions
✔️ Detailed Performance Analysis & Reports
✔️ Aligned with Standard for Program Management – 5th Edition
✔️ 1-Year Access
💡 Built for aspirants who want to:
✅ Simulate the real exam environment
✅ Improve time management
✅ Identify gaps and boost confidence

Prepare like it’s the real exam with PgMP Challenger Gold – your trusted tool for PgMP® certification success in 2025.
View our upcoming PgMP Programs
Online – http://bit.ly/2oBKQXQ
Direct – http://bit.ly/2oCfpg0
How to clear PgMP in first attempt – https://bit.ly/2Yo7EvQ
Need guidance? Book a FREE 15-min Consultation with Dharam Singh PfMP, PgMP, PMP, PMOCP, PBA, SP, RMP, ACP, DASM, DASSM, PMI-ATP, leading PMP, PgMP & PfMP Mentor: 🔗 talktodharam.com
📞 +1 9722927588
🌐 vcareprojectmanagement.com
#PgMP #PgMPMockExams #PgMPChallengerGold #PgMPSimulator #PgMP2025 #PgMPPreparation #ProgramManagement #PMICertifications #ProjectManagementCareer #vCareProjectManagement #SPM5 #PgMPTestPrep #MockExams #PgMPSuccess #DharamSinghMentor #PMIATP #PgMPExamPractice #PgMPStudyTools #PgMPBootcamp #ProgramManagementTools
by vCare Project Management CW | Jun 20, 2025 | Leadership in Project Management, Program Management, Project Management, Strategic Management and Alignment
Turning 55 makes me reflect on a journey built not just on time, but on projects, people, and a purpose that has guided me throughout. From a hands-on practitioner to a worldwide mentor directing professionals in navigating their paths in project leadership, this has been a learning-based journey for me.
“A leader is one who knows the way goes the way and shows the way.” – John C. Maxwell

At 55, Dharam reflect on a journey shaped by purpose, people, and global impact in project leadership and mentoring.
As the field of project management is evolving rapidly, bringing both complex challenges and exciting opportunities. Professionals often begin their journey with foundational credentials such as CAPM®, PMI Project Management Ready™, and PMI Kickoff™, which provide a solid base for advanced certifications like PMP®. As they grow in expertise and responsibility, many pursue specialized credentials such as PgMP® for program management and PfMP® for strategic portfolio management, emphasizing leadership, strategic thinking, and technical proficiency.
To further strengthen capabilities in PMO management and organizational alignment, PMI has recently launched the PMO Certified Professional (PMOCP)™. Collectively, these certifications offer a structured pathway for developing resilient, future-ready leaders equipped to navigate today’s dynamic project landscape.
Reflecting at 55: A Journey Built on Projects, People, and Purpose
I still find myself thinking about some basic concerns even after all these years of project, program, and portfolio management experience. These are not merely questions; rather, they are reflective thoughts that help me stay grounded, receptive to ongoing learning, and in line with the dynamic nature of our line of work. They remind us that no matter how far we’ve come, growth is an ongoing process. These important questions keep coming to mind:
1. How do I stay truly relevant in today’s fast-changing project world?
2. What really makes a mentor different from a practitioner in project leadership?
3. Can a career build on purpose last longer than one focused only on results?
4. What kind of mind-set does someone need to succeed in earning PgMP® or PfMP® certification?
5. How do I keep growing when the industry, tools, and expectations are always evolving?

At 55, Dharam Singh reflects on the timeless questions that continue to shape great project leaders and mentors.
These questions shape the way I lead and mentor. They influence how I train, how I support aspirants, and how I walk alongside them on their certification journey. I believe these are not just personal reflections, but essential questions that every committed project leader must explore as they progress in their professional path.
From Practitioner to Global Mentor: My Evolution in Project Leadership
When I started my journey in project management, my focus was on project delivery. I concentrated on meeting deadlines, achieving goals, and satisfying stakeholders. Over time, as I led diverse teams and handled complex programs across sectors, my perspective began to shift. I started to value the power of strategic alignment and the human side of leadership. One of my most meaningful moments came when a former trainee told me that earning their PgMP® changed their entire career path. That made me realize mentorship was not just support, it was impact.
Becoming a global mentor was never part of a grand plan. It happened as I shared lessons, simplified complex concepts, and helped others unlock their potential. Today, I guide aspirants not only through certification paths but through mind-set transformation. I remind them that leadership is not about control, but about clarity, consistency, and contributing to the growth of others.
PgMP® and PfMP®: More Relevant Than Ever in Today’s Project Economy
Certifications like PgMP® and PfMP® have become increasingly important in today’s dynamic project environment. They not only validate advanced project leadership but also represent a professional’s commitment to driving impactful change in an innovation-driven world. These certifications empower professionals with strategic thinking, cross-functional leadership, and the ability to deliver results aligned with organizational goals.
PgMP® – Program Management Professional
The PgMP® credential is tailored for professionals managing multiple, related projects and achieving strategic objectives. It reflects leadership at a higher level, beyond individual project delivery.
Key aspects are:
• It focuses on managing complex programs and aligning them with strategic goals.
• It emphasizes benefits realization and stakeholder alignment.
• PgMP® is ideal for experienced project managers ready to scale up to program leadership.
Global Impact of vCare Project Management in PgMP® certification are:
1. North America
• United States: 11.2%
• Canada: 9.7%
• Mexico: 12.0%
2. Asia & Middle East
• India: 14.5%
• Saudi Arabia: 5.5%
• United Arab Emirates: 13.4%
• Singapore: 14.3%
• Malaysia: 26.0%
• Kuwait: 7.7%
3. Oceania
• Australia: 35.0%
• New Zealand: 35.0%
4. Europe
• Germany: 13.75%
• Italy: 17.2%

From practitioner to global mentor—Dharam Singh reflects on a leadership journey rooted in purpose and impact.
PfMP® – Portfolio Management Professional
The PfMP® credential is designed for senior professionals who manage portfolios of programs and projects aligned with strategic business objectives.
Key Highlights:
• It focuses on portfolio strategy, governance, performance, and risk management.
• It equips leaders to prioritize initiatives and optimize investments.
• It is ideal for executives and portfolio managers driving organizational value.
Global Impact of vCare Project Management in PfMP®:
1. North America
• United States: 10.0%
• Canada: 12.0%
2. Asia & Middle East
• Saudi Arabia: 3.4%
• India: 6.0%
• United Arab Emirates: 8.8%
• Qatar: 23.8%
• China, mainland: 1.5%
3. Oceania
• Australia: 50.0%
• New Zealand: 66.6%
4. Europe
• Germany: 18.8%
• Greece: 33.3%

PfMP equips senior professionals to align portfolios with strategy and drive high-impact results—see how vCare supports global leaders in this mission.
These vCare contribution percentages clearly highlight the organization’s strong global presence and its impactful role in shaping certified leaders across continents.
According to the PMI Registry, the global certification landscape shows that China has approximately 2580+ PgMP’s and the United States has approximately 1500+ PgMP’s and these are the top two countries in the world for PgMP® certifications, reflecting their deep investment in advanced program management capabilities. When it comes to PfMP®, the The United States continues to lead globally with approximately 574+ PfMPs, while Saudi Arabia, now in second place with around 564+, is rapidly closing the gap in its push to become the global leader in strategic portfolio management.
Against this global backdrop, vCare’s consistent mentoring excellence continues to empower professionals to not only earn these elite credentials but to lead with clarity, confidence, and purpose.
The Certification Mindset: Forging Resilient, Strategic Leaders for a Complex World
PgMP® and PfMP® certificates can change the way professionals think, which helps them lead with foresight, deal with complexity, and make sure that projects are in line with the goals of the organisation. This way of thinking promotes learning for life, self-control, and being open to change. It also helps people become stronger, by teaching them how to deal with uncertainty, stay focused, and think critically. Certified leaders are renowned for their expertise and the way they use it in a world where things are always evolving, breakdown, and generating new concepts. You must think like this if you want to be a successful leader and remain relevant for a long time.
AI in Project Management: Disruptor, Enabler, or Strategic Partner?
AI is transforming the project management environment across various sectors, with experts unsure whether it is a strategic partner, enabler, or disruptor. However, when approached with knowledge and preparedness, AI becomes a strong facilitator, automating operations, boosting risk management, and streamlining resource planning. This allows project managers to focus on higher-value work, such as strategic decision-making, innovation, and stakeholder engagement.
AI makes consistent decision-making easier, implementation faster, and reduces complexity. Real-time data insights help teams work more efficiently and adapt quickly. Incorporating AI tools into daily project processes is essential for modern project ecosystems, reducing manual errors, improving accuracy, and ensuring on-time delivery.
AI can handle and analyze large amounts of data, but ethical supervision, context, and direction still rely on human leadership. Merging artificial intelligence with human insight leads to better outcomes, imagination, and strong project plans. Project managers must appreciate the possibilities of AI and use it appropriately, as those who see AI as an enabler of smarter, more agile project management rather than a threat will be ideally positioned to lead the next generation of high-performing, technology-driven projects.
Staying Human in the Age of AI: Essential Practices for Project Leaders
The role of a project leader, in my opinion, becomes even more human-centric as AI continues to change the field of project management. I adhere to the following crucial procedures and advise others who want to lead successfully in this AI-driven age:
1. Stress the importance of emotional intelligence and empathy – Make a human connection with your teammates. The emotional depth needed to inspire and establish trust cannot be replaced by technology.
2. Pay attention to stakeholder communication – Leaders need to manage relationships while AI handles data. Communication that is honest, transparent, and compassionate is still essential.
3. Combine judgement and data – Utilise AI-generated insights, but always use human judgement to understand long-term effects, context, and values.
4. Establish a culture of education – Teams should be encouraged to remain inquisitive and receptive to advancements in technology and people.
5. Encourage morality and diversity – Make sure AI-powered decisions are impartial, open, and consistent with moral principles.
6. Set a good example – Exhibit resilience, humility, and flexibility. More than any algorithm, these human qualities motivate teams.
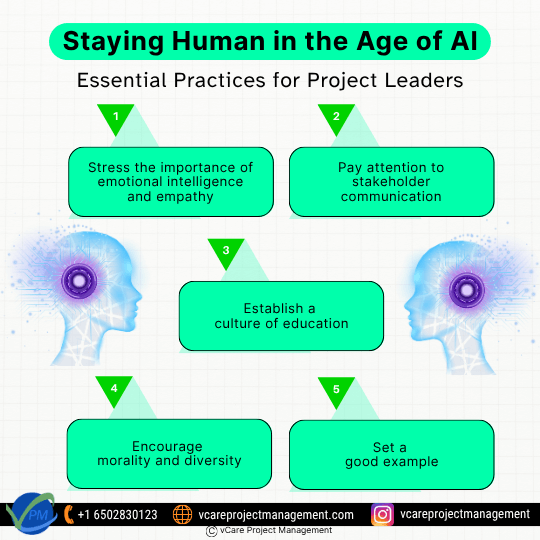
AI is reshaping project management, but empathy, ethics, and human judgement are what set great leaders apart.
The goal of remaining human is not to oppose AI. It involves balancing it with the enduring principles of leadership – vision, integrity, and compassion.
How PMI’s PMO Certification (PMOCP) Is Shaping the Future of Project Management Offices
I consider the PMI-PMOCP™ to be a strategic and timely development for PMO professionals. By coordinating project execution with overarching business objectives, the PMI PMOCP™ certification aims to identify and enable strategic PMO leadership. It emphasises practical, real-world skills like influence, agility, governance, and stakeholder engagement, all of which are critical in today’s changing environments.
By equipping professionals to lead significant organisational change rather than merely concentrating on status updates, it also fills important skill gaps in today’s PMOs. I gave a thorough rundown of the exam structure, application procedure, and efficient study methods in our most recent vCare webinar.
Having the PMOCP™ certification improves one’s reputation internationally and opens doors in various sectors and geographical areas. This certificate helps professionals land important roles and make strategic contributions to their organisations, whether they are creating a new PMO or expanding an existing one.
vCare Project Management is hosting a special webinar on the PMI-PMOCP™. The session features Kim Marcelliano, Senior Product Manager at PMI. She will share strategic insights on the credential’s relevance and target audience, while I will explain the exam structure, application process, and preparation tips. With their combined expertise, the webinar offers a clear path to PMO certification success. Ideal for PMO leaders and aspiring professionals, this session will provide valuable guidance to advance your career and strengthen your PMO’s strategic impact. So, don’t miss this opportunity, do check the webinar if you are interested.

PMI-PMOCP is redefining PMO leadership. Learn how this new certification aligns strategy, agility, and impact.
Register Now: https://bit.ly/3Sp9h5l
Date: Wednesday, 02nd July 2025
Time: 10:00 AM – 11:00 AM (PDT) / 11:00 AM – 12:00 PM (MDT) / 12:00 PM – 01:00 PM (CDT) / 01:00 PM – 02:00 PM (EDT) / 02:00 PM – 03:00 PM (BRT) / 07:00 PM – 08:00 PM (CEST) / 08:00 PM – 09:00 PM (AST) / 09:00 PM – 10:00 PM (GST) / 10:30 PM – 11:30 PM (IST)
Guiding the Next Generation: My Approach to PgMP® and PfMP® Mentoring
Being a mentor is not just what I do, it’s what keeps me growing. Every interaction teaches me something new. While I have had the privilege of guiding over 570 PgMP®s and 177 PfMP®s worldwide, I consider myself a co-learner in this journey, growing alongside every professional I mentor.
PgMP® and PfMP® are more than just certifications. They stand for advanced governance skills, strategic thinking, and the capacity to match organizational objectives with program and portfolio objectives. The need for leaders with this degree of experience is growing as the project economy develops. These qualifications are increasingly crucial indicators of leadership prepared for the future.
Making this journey both meaningful and attainable is our mission at vCare Project Management. With tested mentoring models, organized preparation programs, and continuous support, we give candidates a clear path forward. Our goal is to help you pass, but we also want to help you become more confident and clear-headed in the process.
I provide advice to each person I mentor based on practical difficulties and knowledge gathered over many years of experience. There is no shortcut to success in PgMP® or PfMP®. It all comes down to comprehension, attitude, and steady support.
vCare Project Management can help you make the next big career move with purpose and precision.
The Road Ahead: Lifelong Learning and Collective Growth Beyond 55
As I turn 55, it feels perfectly timed that I have had the privilege of mentoring over 555+ aspirants, one for every year of my life and a few extra for good measure.
But a journey doesn’t end when you turn 55, but it marks the start of a new chapter based on in-depth education, significant mentoring, and a mutual dedication to the advancement of the field. There is a greater need than ever for strategic, forward-thinking leaders as the project landscape changes quickly and artificial intelligence changes how we lead and deliver.
There are still not many PgMP® and PfMP® certified professionals in the world, there are only 2500 PfMP®’s and 7900 PgMP®’s. Aspiring professionals have a significant opportunity here. These certifications represent more than just accomplishments. They serve as indicators of maturity, foresight, and the capacity to influence programs and portfolios.
“The function of leadership is to produce more leaders, not more followers.” – Ralph Nader
As Dharam Singh turns 55, he reflects on mentoring 555+ leaders and shaping the future of project and portfolio excellence.
Our goal at vCare Project Management is to enable people by providing them with organised mentoring, insightful guidance, and constant encouragement. We assist professionals in developing their leadership skills as well as their knowledge.
Now is a good time to think about your next project leadership move. The world needs competent, qualified individuals who are prepared to lead with clarity and purpose. At vCare, we are ready to provide you with forthright and specialist support during that journey.
Note: The figure of globally certified PgMPs & PfMPs is a guestimate based on available public sources and professional observations. Actual numbers may vary as PMI does not always publish real-time global certification data.
#DharamSingh #55YearsOfPurpose #PgMP #PfMP #PMOCP #ProjectLeadership #vCareProjectManagement #MentorshipMatters #StrategicPMO #AIandLeadership #PMICertification #FutureOfPMO #ProjectEconomy #PortfolioManagement #GlobalMentor #LeadershipReflection #LifelongLearning #EmotionalIntelligence #ProjectManagement

by vCare Project Management CW | Jun 16, 2025 | Portfolio Management, Professional Development Webinars, Program Management, Project Management
Join vCare Project Management for an exclusive webinar featuring Jay Brough, PfPM, PgPM, PMP, LSSBB a distinguished Army veteran and program management leader from Frankfort, Kentucky, USA. Hosted by Dharam Singh PfMP, PgMP, PMP, PMOCP, PBA, SP, RMP, ACP, DASM, DASSM, PMI-ATP of vCare Project Management and a globally recognized mentor in PMP, PgMP, and PfMP, this session will provide valuable insights into leadership, operational efficiency, and strategic transformation across various industries.
Title: “Strategic Leadership & Operational Excellence”
🔗 Reserve your spot now: https://bit.ly/41sSraX
Session Date : Thursday, 26 June 2025
Session Time:
08:00 AM – 09:00 AM (PDT) / 09:00 AM – 10:00 AM (MDT)
10:00 AM – 11:00 AM (CDT) / 11:00 AM – 12:00 PM (EDT)
12:00 PM – 01:00 PM (BRT) / 04:00 PM – 05:00 PM (BST)
05:00 PM – 06:00 PM (CEST) / 06:00 PM – 07:00 PM (AST)
07:00 PM – 08:00 PM (GST) / 08:30 PM – 09:30 PM (IST)
Key topics include:
– Bridging Military Leadership with Corporate Agility
– Ensuring Operational Security & Compliance in a Cyber-Threat Landscape
– The Role of AI in Strategic Decision-Making
– Crisis Leadership: Lessons from the Military for Corporate Resilience
– Universal Leadership Strategies Across Sectors
Don’t miss this opportunity to earn 1 PDU, gain valuable career and certification insights, and benefit from an exclusive discount on vCare Project Management’s upcoming PMP, PgMP, and PfMP programs. Secure your spot today!
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with Dharam Singh, leading PMP, PgMP, & PfMP Mentor by visiting https://lnkd.in/gU79KD4K
Subscribe for More:
Success Stories | Q&A: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
Podcasts and Interviews: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#ProjectManagement #PgMP #PfMP #PMP #PMICertifications #JayBrough #USMilitary #USA #ProjectManagementProfessional #PgMP4U #PfMP4U #PMI #PMIWebinar #PDU

by vCare Project Management CW | Jun 9, 2025 | Portfolio Management, Program Management, Project Management, vCare PMI Certification Training Classes
🎯 Join Our PMI Certification Bootcamps – June 2025 | Dallas, Texas, USA
Are you ready to take your program or portfolio leadership to the next level?
vCare Project Management is proud to present two exclusive, in-person bootcamps in Dallas this June – led by PMI-ATP Mentor Dharam Singh, who has guided 558+ PgMP®s and 176+ PfMP®s worldwide.
📍 Location: Dallas, Texas, United States
🎓 Trainer: Dharam Singh PfMP, PgMP, PMP, PMOCP, PBA, SP, RMP, ACP, DASM, DASSM, PMI-ATP – Leading PMP®, PgMP®, PfMP® Mentor | vCare Project Management
🔹 Program Management Certification Training (PgMP®)
📅 20–22 June 2025, 9 AM – 5 PM CDT
🔗 https://bit.ly/3BGZeUh
🔹 Portfolio Management Certification Training (PfMP®)
📅 27–29 June 2025, 9 AM – 5 PM CDT
🔗 https://bit.ly/3ByLdrs
📌 Seats are limited – secure your spot and fast-track your PMI certification journey today!

Join our exclusive PgMP & PfMP Bootcamps in Dallas this June – In-person PMI certification training with Dharam Singh. Limited seats!
🚀 Exclusive Offers & Discounts on Training Programs!
👉 Check out special offers here: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
🎯 Not Sure If You’re Ready? Let’s Talk!
💡 Book a FREE 15-min Consultation with Dharam: 🔗 http://talktodharam.com
📺 Stay Ahead in Project Management!
🔔 Subscribe to vCare Project Management YouTube Channel: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
🎙 Follow Dharam Podcasts & Expert Interviews: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#PgMP #PfMP #PMICertification #ProgramManagement #PortfolioManagement #DharamSingh #vCareProjectManagement #DallasBootcamp #LeadershipTraining #PMO #StrategicLeadership #PMIATP #DirectBootcamp #USAEvents #June2025


























